Prostate segmentation and surface reconstruction
This page contains instructions on how to perform MRI prostate segmentation and surface reconstruction in MIPAV. The algorithm facilities the validation of multi-parametric MRI with histopathology slides from radical prostatectomy specimens and targeted biopsy specimens. It employs the technique that combines image processing and computer aided design to construct a high resolution 3D prostate surface from MRI images in three orthogonal views with non-isotropic voxel resolution.
The algorithm outline is shown below (TBD).
Contents
Image types
The algorithm could be applied to the following image types (TBD).
Sample image dataset
The sample image dataset can be downloaded using this link (TBD). The data included into the data set are MR images obtained from a 3.0 T whole-body MRI system (Achieva, Philips Healthcare).
T2-weighted MR images of the entire prostate were obtained in three orthogonal planes (sagittal, axial and coronal) using the following settings:
- Scan resolution of 0.2734x0.2734x3.0 cubic millimeters,
- Field of view - 140 mm,
- Image slice dimension 512x512.
The center of the prostate is the focal point for the MRI scan. To reduce the scan time, a lower refocusing pulse of 100 degrees was used for sagittal and coronal images, which alters the contrast on these images compared to the axial images.
Applying the algorithm
Applying the algorithm involves the following steps:
- Opening 3 orthogonal images and delineating VOIs (manually or using VOI from the the test image dataset);
- Prostate segmentation using Automatic B-Spline Registration algorithm;
- Prostate surface reconstruction;
- 3D Visualization and STL surface generation.
Opening images and delineating VOIs
Axial image
Open an axial image. Use File > Open image (A) from disk menu. If you are using the test image dataset provided, open the img_ax_83.xml file.
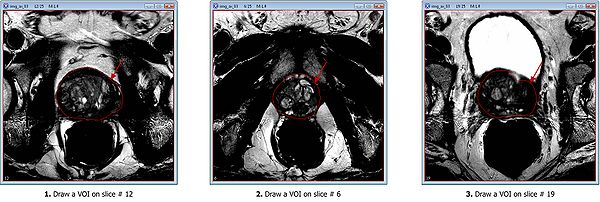
Draw 3 polygon/polyline VOIs. Use the Polygon/Polyline VOI tool ![]() from the MIPAV toolbar.
from the MIPAV toolbar.
For example, for the test image dataset provided:
- Draw the mid slice VOI first, on slice #12;
- Then draw the apex VOI, on slice #6;
- And finally, draw the last VOI on the base slice #19.
Smooth VOIs
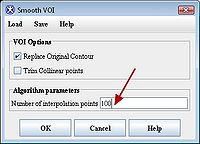
After delineating VOIs, we need to smooth each VOI. In order to do this, select each VOI and call the Smooth VOI dialog box available from the main MIPAV menu (VOI > Smooth VOI).
In the Smooth VOI dialog box, check the "Replace Original Contour" box, and set "Number of interpolation points" to 100. Click “OK”. Repeat for all 3 contours.
Sagittal and coronal images
Repeat the same process of delineating and smoothing VOIs for both sagittal and coronal images. for the test image dataset provided, the saggital image is img_sag_83.xml and the coronal image is img_cor_83.xml.
Example
In the image provided, VOIs files are already available for all 3 types of images (axial, saggital and coronal). Under the image dataset directory, one can find 3 orthogonal images and corresponding VOIs:
| Orientation | Image file | VOI file |
|---|---|---|
| axial | img_ax_83.xml | voi_ax_83.xml |
| coronal | img_cor_83.xml | voi_cor_83.xml |
| saggital | img_sag_83.xml - saggital | voi_sag_83.xml |
Corresponding VOIs are as follows:
- voi_ax_83.xml
- voi_cor_83.xml,
- voi_sag_83.xml.
Those VOIs were drawn by clinical researchers, and verified by radiologist expert at NCI. For experimental purposes, we perform quick VOIs copying instead of drawing the three VOIs to save time.
With MIPAV, open the same image twice, and open the VOIs file in the extra opened image. From MIPAV toolbar, use the images link tool ( ) to link the two images. Please, make sure to match the same image slice, i.e. 12, before you click the link button. Then, you can slide through the two images in parallel mode. Copy the three VOIs from extra opened image to the source image. Don’t forget the sequence order, mid->start->end. Select all VOIs, use smooth dialog to smooth the VOIs contours to 100 points. After finish copying the three VOIs, click the link button ( ) again to unlink the two images, and close the extra opened image. Repeat the same procedure for all three, axial, sagittal and coronal images. Figure 6 shows the linked images mode.