Difference between revisions of "MIPAV system requirements"
m (→GPU computing) |
m (→GPU computing) |
||
| (7 intermediate revisions by 3 users not shown) | |||
| Line 12: | Line 12: | ||
=== Hard drive space requirements === | === Hard drive space requirements === | ||
| − | A minimum of 25 MB free hard disk space plus | + | A minimum of 25 MB free hard disk space plus an additional image file storage space - MIPAV software components require 25 MB of hard disk space for storage. If you plan to store image files on your hard disk, you need to allocate more space. |
[[Category:Help]] | [[Category:Help]] | ||
| Line 19: | Line 19: | ||
== GPU computing == | == GPU computing == | ||
| − | GPU computing is the use of a graphics processing unit (GPU) as a co-processor to accelerate CPUs for image processing, scientific, and engineering computing. | + | ''See also:'' [[Volume renderer GPU support listing]]. |
| − | The GPU accelerates applications by taking some of the compute-intensive and time consuming portions of the code from the CPU and running it. In that case both GPU and CPU share the same code execution | + | |
| + | GPU computing is the use of a graphics processing unit (GPU) as a co-processor to accelerate CPUs for image processing, scientific, and engineering computing. The GPU accelerates applications by taking some of the compute-intensive and time consuming portions of the code from the CPU and running it itself. In that case both GPU and CPU share the same code execution. As a result, the application runs faster because in addition to CPU it also uses the massively parallel processing power of the GPU. This is also known as “heterogeneous” or “hybrid” computing or [http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/GPGPU GP-GPU computing]. | ||
Normally, a CPU consists of four to eight cores, while the GPU consists of hundreds of smaller cores. When used together, they provide a higher computational performance, which is important for medical image analysis. | Normally, a CPU consists of four to eight cores, while the GPU consists of hundreds of smaller cores. When used together, they provide a higher computational performance, which is important for medical image analysis. | ||
| Line 27: | Line 28: | ||
MIPAV uses GPU computing to run its [[Volume Renderer]] and also in the [[DTI Pipeline | DTI Pipeline Visualization]]. See also [http://144.206.159.178/ft/CONF/16412650/16412654.pdf Cheng 2006]. | MIPAV uses GPU computing to run its [[Volume Renderer]] and also in the [[DTI Pipeline | DTI Pipeline Visualization]]. See also [http://144.206.159.178/ft/CONF/16412650/16412654.pdf Cheng 2006]. | ||
| − | In order to run MIPAV GPU based Volume Renderer, | + | In order to run MIPAV GPU based Volume Renderer, an NVIDIA video card and the proper video card driver need to be installed: |
<ol> | <ol> | ||
| − | <li>Install the corresponding [http://www.nvidia.com/ NVIDIA driver] which uses | + | <li>Install the corresponding [http://www.nvidia.com/ NVIDIA driver] which uses [http://www.khronos.org/opencl/ OpenCL ver 1.2]. Select the driver from the [http://www.nvidia.com/Download/index.aspx?lang=en-us NVIDIA web site];</li> |
<li> Enable GPU computing in the [[Customizing MIPAV#OtherTab | MIPAV Options dialog box]].</li> | <li> Enable GPU computing in the [[Customizing MIPAV#OtherTab | MIPAV Options dialog box]].</li> | ||
</ol> | </ol> | ||
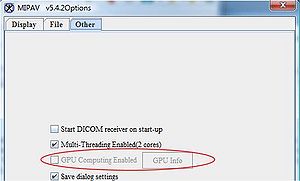
| − | '''Note:''' if the GPU | + | '''Note:''' if the GPU Computing Enabled option is grayed out in the [[Customizing MIPAV#OtherTab | MIPAV Options - Other]] dialog box, that means that either a video card driver or a video card needs an upgrade, or they both need it. |
== Memory requirements == | == Memory requirements == | ||
| Line 41: | Line 42: | ||
'''Minimal requirements:''' MIPAV requires a base of 35 MB of RAM. However, when you open an image file, MIPAV requires additional memory to correctly display the file and quantify data. | '''Minimal requirements:''' MIPAV requires a base of 35 MB of RAM. However, when you open an image file, MIPAV requires additional memory to correctly display the file and quantify data. | ||
| − | + | ||
[[Category:Help]] | [[Category:Help]] | ||
| Line 48: | Line 49: | ||
To more precisely determine the amount of memory that you need, estimate the number of files you generally have open at one time. Next, add the sizes of the files together and multiply the result by 10. <br /> | To more precisely determine the amount of memory that you need, estimate the number of files you generally have open at one time. Next, add the sizes of the files together and multiply the result by 10. <br /> | ||
| − | |||
During a typical MIPAV session, you might generally compare and contrast three image files. The estimated file sizes may be 2 MB, 4.5 MB, and 6 MB. The calculation would be: 10(2 8.5 10) 35 = 240. Thus, in this scenario, you need 240 MB of a combination of RAM and virtual memory to run MIPAV and visualize the three image files. Note that for DICOM datasets you must add all of the files in the dataset, even if you only work with one or two images.<br /> | During a typical MIPAV session, you might generally compare and contrast three image files. The estimated file sizes may be 2 MB, 4.5 MB, and 6 MB. The calculation would be: 10(2 8.5 10) 35 = 240. Thus, in this scenario, you need 240 MB of a combination of RAM and virtual memory to run MIPAV and visualize the three image files. Note that for DICOM datasets you must add all of the files in the dataset, even if you only work with one or two images.<br /> | ||
| − | + | If you need to allocate more than 100MB of memory, after you install MIPAV you need [[Allocating Memory in MIPAV|to adjust the memory allocation settings]]. | |
| − | If you need to allocate more than 100MB of memory, after you install MIPAV you need to adjust the memory allocation settings. | + | |
==See also: == | ==See also: == | ||
| Line 60: | Line 59: | ||
[[Getting Started Quickly with MIPAV]] | [[Getting Started Quickly with MIPAV]] | ||
[[Customizing MIPAV]] | [[Customizing MIPAV]] | ||
| − | |||
[[Category:Help]] | [[Category:Help]] | ||
Latest revision as of 17:00, 18 June 2013
Because MIPAV is Java-based, it can run on many different platforms, such as Windows (Vista, XP, NT, 95, 98, and 2000), Solaris, Linux, UNIX, Macintosh, and SGI workstation.
Contents
Understanding the system requirements
System requirements
MIPAV now requires Java 1.6 or higher to run.
MIPAV runs optimally on a system with Pentium III 400-megahertz (MHz) processor. Although MIPAV can run on a computer with a slower processor speed, for peak performance a processor that is equivalent to or faster than Pentium III 400 MHz is recommended.
Hard drive space requirements
A minimum of 25 MB free hard disk space plus an additional image file storage space - MIPAV software components require 25 MB of hard disk space for storage. If you plan to store image files on your hard disk, you need to allocate more space.
GPU computing
See also: Volume renderer GPU support listing.
GPU computing is the use of a graphics processing unit (GPU) as a co-processor to accelerate CPUs for image processing, scientific, and engineering computing. The GPU accelerates applications by taking some of the compute-intensive and time consuming portions of the code from the CPU and running it itself. In that case both GPU and CPU share the same code execution. As a result, the application runs faster because in addition to CPU it also uses the massively parallel processing power of the GPU. This is also known as “heterogeneous” or “hybrid” computing or GP-GPU computing.
Normally, a CPU consists of four to eight cores, while the GPU consists of hundreds of smaller cores. When used together, they provide a higher computational performance, which is important for medical image analysis.
MIPAV uses GPU computing to run its Volume Renderer and also in the DTI Pipeline Visualization. See also Cheng 2006.
In order to run MIPAV GPU based Volume Renderer, an NVIDIA video card and the proper video card driver need to be installed:
- Install the corresponding NVIDIA driver which uses OpenCL ver 1.2. Select the driver from the NVIDIA web site;
- Enable GPU computing in the MIPAV Options dialog box.
Note: if the GPU Computing Enabled option is grayed out in the MIPAV Options - Other dialog box, that means that either a video card driver or a video card needs an upgrade, or they both need it.
Memory requirements
At least 100 Megabytes (MB) of a combination of random access memory (RAM) and virtual memory (recommended). By default, MIPAV allocates 100 MB of a combination of RAM and virtual memory. However, your own memory requirements may differ.
Minimal requirements: MIPAV requires a base of 35 MB of RAM. However, when you open an image file, MIPAV requires additional memory to correctly display the file and quantify data.
How to determine the amount of memory you need to run MIPAV
To more precisely determine the amount of memory that you need, estimate the number of files you generally have open at one time. Next, add the sizes of the files together and multiply the result by 10.
During a typical MIPAV session, you might generally compare and contrast three image files. The estimated file sizes may be 2 MB, 4.5 MB, and 6 MB. The calculation would be: 10(2 8.5 10) 35 = 240. Thus, in this scenario, you need 240 MB of a combination of RAM and virtual memory to run MIPAV and visualize the three image files. Note that for DICOM datasets you must add all of the files in the dataset, even if you only work with one or two images.
If you need to allocate more than 100MB of memory, after you install MIPAV you need to adjust the memory allocation settings.
See also:
Installing mipav Getting Started Quickly with MIPAV
Customizing MIPAV