Creating new images and Generating graphs: Difference between pages
MIPAV>Olgavovk |
MIPAV>Angelfish100 |
||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
MIPAV allows you to generate intensity profiles, or contour VOI graphs, for VOI contours. For delineated VOIs, you can generate 2D, 3D, or 4D intensity graphs. You can also generate a 3D intensity graph at a specific point across all slices in a dataset. For information on how to contour a VOI, refer to Chapter 1, "Segmenting Images Using Contours and Masks,"<br /> | |||
=== Generating contour VOI graphs === | |||
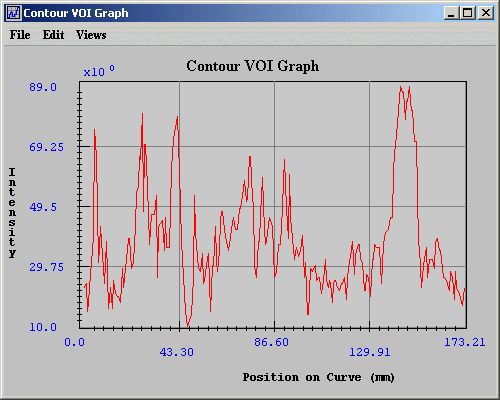
Contour VOI graphs display the intensity values of the selected contour's boundary in the Contour VOI Graph window (Figure 10). You can generate either 2D or 3D contour VOI graphs. <br /> | |||
'''To generate 2D contour VOI graphs'''<br /> | |||
1 Open an image.<br /> | |||
2 Delineate a 2D VOI on the image using one of the 2D icons in the MIPAV window.<br /> | |||
< | |||
{| border="1" cellpadding="5" | {| border="1" cellpadding="5" | ||
|+ < | |+ '''Figure 10. Contour VOI Graph window ''' | ||
|- | |||
| rowspan="1" colspan="3" | | |||
[[Image:windowContourVOIGraph.jpg]] | |||
|- | |||
| rowspan="4" colspan="1" | | |||
<div class="CellBody"><span style="font-style: normal; text-decoration: none; text-transform: none; vertical-align: baseline">'''<font color="#000000">File</font>'''</span></div> | |||
| rowspan="1" colspan="2" | | |||
<div class="CellBody"><span style="font-style: normal; text-decoration: none; text-transform: none; vertical-align: baseline">'''<font color="#000000">Open Graph</font>'''</span>-Opens a PLT file that contains graph data. When you select this command or press Ctrl O on the keyboard, the Open Graph Data dialog box appears. </div> | |||
|- | |||
| rowspan="1" colspan="2" | | |||
<div class="CellBody"><span style="font-style: normal; text-decoration: none; text-transform: none; vertical-align: baseline">'''<font color="#000000">Save Graph</font>'''</span>-Saves the graph data in a PLT file. When you select this command or when you press Ctrl S on the keyboard, the Save dialog box opens.</div> | |||
|- | |||
| rowspan="1" colspan="2" | | |||
<div class="CellBody"><span style="font-style: normal; text-decoration: none; text-transform: none; vertical-align: baseline">'''<font color="#000000">Print Graph</font>'''</span>-Allows you to print the graph. When you select this command or press <br />Ctrl P, the Print dialog box opens.</div> | |||
|- | |- | ||
| rowspan="1" colspan="2" | | | rowspan="1" colspan="2" | | ||
<div class="CellBody"><span style="font-style: normal; text-decoration: none; text-transform: none; vertical-align: baseline">'''<font color="#000000">Close Graph</font>'''</span>-Closes the Intensity Graph window. To close the window, you can also press Ctrl X on the keyboard.</div> | |||
''' | |||
|- | |- | ||
| | | rowspan="3" colspan="1" | | ||
''' | <div class="CellBody"><span style="font-style: normal; text-decoration: none; text-transform: none; vertical-align: baseline">'''<font color="#000000">Edit</font>'''</span></div> | ||
| rowspan="1" colspan="2" | | | rowspan="1" colspan="2" | | ||
<div class="CellBody"><span style="font-style: normal; text-decoration: none; text-transform: none; vertical-align: baseline">'''<font color="#000000">Delete Function</font>'''</span>-Allows you to delete a specific function. However, you cannot delete a function if it is the only function displayed in the window.</div> | |||
|- | |- | ||
| rowspan="1" colspan="2" | | | rowspan="1" colspan="2" | | ||
<div class="CellBody"><span style="font-style: normal; text-decoration: none; text-transform: none; vertical-align: baseline">'''<font color="#000000">Copy Function</font>'''</span>-Copies a function that is currently displayed in the window.</div> | |||
|- | |- | ||
| rowspan="1" colspan="2" | | | rowspan="1" colspan="2" | | ||
<div class="CellBody"><span style="font-style: normal; text-decoration: none; text-transform: none; vertical-align: baseline">'''<font color="#000000">Paste Function</font>'''</span>-Pastes a previously copied function into the window. The pasted function has a different color than the first function displayed in the window.</div> | |||
|- | |- | ||
| | | rowspan="3" colspan="1" | | ||
<div class="CellBody"><span style="font-style: normal; text-decoration: none; text-transform: none; vertical-align: baseline">'''<font color="#000000"> | <div class="CellBody"><span style="font-style: normal; text-decoration: none; text-transform: none; vertical-align: baseline">'''<font color="#000000">Views</font>'''</span></div> | ||
| rowspan="1" colspan="2" | | | rowspan="1" colspan="2" | | ||
<div class="CellBody"><span style="font-style: normal; text-decoration: none; text-transform: none; vertical-align: baseline">'''<font color="#000000">Modify Graph Features</font>'''</span>-Allows you to customize the appearance of the graph.</div> | |||
|- | |- | ||
| rowspan="1" colspan="2" | | | rowspan="1" colspan="2" | | ||
<div class="CellBody"><span style="font-style: normal; text-decoration: none; text-transform: none; vertical-align: baseline">'''<font color="#000000">Reset Range to Default</font>'''</span>-<span style="font-style: normal; text-decoration: none; text-transform: none; vertical-align: baseline">'''<font color="#000000">[TBD]</font>'''</span></div> | |||
|- | |- | ||
| rowspan="1" colspan="2" | | | rowspan="1" colspan="2" | | ||
> | <div class="CellBody"><span style="font-style: normal; text-decoration: none; text-transform: none; vertical-align: baseline">'''<font color="#000000">Reset Graph to Original</font>'''</span>-<span style="font-style: normal; text-decoration: none; text-transform: none; vertical-align: baseline">'''<font color="#000000">[TBD]</font>'''</span>. </div> | ||
|- | |- | ||
| | | | ||
'''Help''' | <div class="CellBody"><span style="font-style: normal; text-decoration: none; text-transform: none; vertical-align: baseline">'''<font color="#000000">Help</font>'''</span></div> | ||
| rowspan="1" colspan="2" | | | rowspan="1" colspan="2" | | ||
Displays online help | <div class="CellBody"><span style="font-style: normal; text-decoration: none; text-transform: none; vertical-align: baseline">'''<font color="#000000">Help Topics</font>'''</span>-Displays online help topics.</div> | ||
|} | |} | ||
<br /> | |||
3 Select the VOI. <br /> | |||
As an option, copy the VOI to other slices in the dataset by selecting VOI > Propagate and one of the following commands:<br /> | |||
*To Next Slice<br /> | |||
*To Previous Slice<br /> | |||
*To All Slices<br /> | |||
4 Do one of the following:<br /> | |||
*Select VOI > Graph > Boundary Intensity in the MIPAV window. <br /> | |||
*Right click on the VOI and then select Graph > Boundary Intensity.<br /> | |||
*The Contour VOI Graph window (Figure 10) opens.<br /> | |||
'''To generate 3D contour VOI graphs'''<br /> | |||
1 Open an image.<br /> | |||
2 Delineate a VOI on the image using the 3D rectangular VOI icon, in the MIPAV window. <br /> | |||
3 Select the VOI. <br /> | |||
As an option, copy the VOI to other slices in the dataset by selecting VOI > Propagate and one of the following commands:<br /> | |||
*To Next Slice<br /> | |||
*To Previous Slice<br /> | |||
*To All Slices<br /> | |||
4 Do one of the following:<br /> | |||
*Select VOI > Graph > Boundary Intensity in the MIPAV window.<br /> | |||
*Right-click on the VOI and then select Graph > Boundary Intensity. <br /> | |||
The Contour VOI Graph window (Figure 10) opens. This window displays a graph of the intensity values of the selected contour's boundary. <br /> | |||
=== Generating intensity graphs === | |||
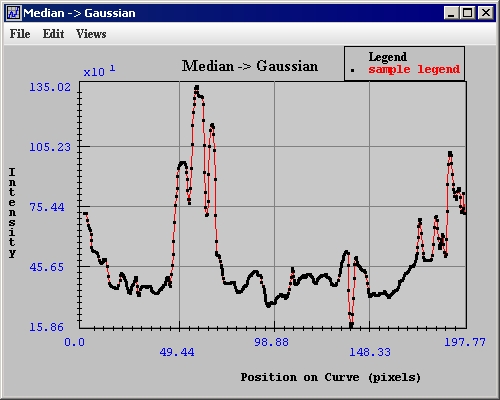
== | Intensity profiles, or graphs, present information on the intensity values of the VOI region in an image. The intensity graph appears in the Intensity Graph window (Figure 11).<br /> | ||
< | '''To generate 2D intensity graphs'''<br /> | ||
1 Open an image.<br /> | |||
< | 2 Delineate a 2D VOI on the image using one of the 2D icons in the MIPAV window.<br />< | ||
3 Select the VOI. <br /> | |||
< | As an option, copy the VOI to other slices in the dataset by selecting VOI > Propagate and one of the following commands:<br /> | ||
< | *To Next Slice<br /> | ||
*To Previous Slice<br /> | |||
< | *To All Slices<br /> | ||
4 Do one of the following:<br /> | |||
Select VOI > Graph in the MIPAV window and either of the following:<br /> | |||
* ''2.5D Total Intensity'' -To generate a graph of the sum of the intensity values of the VOI region. <br /> | |||
* ''2.5D Average Intensity'' -To generate a graph of the average of the intensity values of the VOI region.<br /> | |||
Right-click on the VOI and then select Graph and one of the following commands:<br /> | |||
* ''2.5D Total Intensity'' -To generate a graph of the sum of the intensity values of the area delineated by the VOI per slice.<br /> | |||
* ''2.5D Average Intensity'' -To generate a graph of the average of the intensity values of the VOI region.<br /> | |||
* ''2.5D Total Intensity with Threshold'' -TBD. <br /> | |||
* ''2.5D Average Intensity with Threshold'' -TBD.<br /> | |||
The Intensity Graph window (Figure 11) opens. | |||
{| border="1" cellpadding="5" | {| border="1" cellpadding="5" | ||
|+''' | |+ '''Figure 11. Intensity Graph window ''' | ||
|- | |- | ||
|''' | | | ||
|''' | <div class="CellBody"><span style="font-style: normal; text-decoration: none; text-transform: none; vertical-align: baseline">'''<font color="#000000">File</font>'''</span></div> | ||
| | |||
<div class="CellBody"><span style="font-style: normal; text-decoration: none; text-transform: none; vertical-align: baseline">'''<font color="#000000">Open Graph</font>'''</span>-Opens a PLT file that contains graph data.</div> <div class="CellBody">When you select this command or press Ctrl O on the keyboard, the Open Graph Data dialog box appears. </div> | |||
| rowspan="2" colspan="1" | | |||
[[Image:VOIGRaphMOdifyPointsVis.jpg]] | |||
|- | |- | ||
| | | | ||
|''' | <div class="CellBody"> </div> | ||
| | |||
<div class="CellBody"><span style="font-style: normal; text-decoration: none; text-transform: none; vertical-align: baseline">'''<font color="#000000">Save Graph</font>'''</span>-Saves the graph data in a PLT file. </div> <div class="CellBody">When you select this command or when you press Ctrl S on the keyboard, the Save dialog box opens.</div> | |||
|- | |- | ||
| | | | ||
|''' | <div class="CellBody"> </div> | ||
| rowspan="1" colspan="2" | | |||
<div class="CellBody"><span style="font-style: normal; text-decoration: none; text-transform: none; vertical-align: baseline">'''<font color="#000000">Print Graph</font>'''</span>-Allows you to print the graph. When you select this command or press <br />Ctrl P, the Print dialog box opens.</div> | |||
|- | |- | ||
| | | | ||
|''' | <div class="CellBody"> </div> | ||
| rowspan="1" colspan="2" | | |||
<div class="CellBody"><span style="font-style: normal; text-decoration: none; text-transform: none; vertical-align: baseline">'''<font color="#000000">Close Graph</font>'''</span>-Closes the Intensity Graph window. To close the window, you can also press Ctrl X on the keyboard.</div> | |||
|- | |- | ||
| | | | ||
|''' | <div class="CellBody"><span style="font-style: normal; text-decoration: none; text-transform: none; vertical-align: baseline">'''<font color="#000000">Edit</font>'''</span></div> | ||
| rowspan="1" colspan="2" | | |||
<div class="CellBody"><span style="font-style: normal; text-decoration: none; text-transform: none; vertical-align: baseline">'''<font color="#000000">Delete Function</font>'''</span>-Allows you to delete the function that you select. However, you cannot delete a function if it is the only function displayed in the window.</div> | |||
|- | |- | ||
| | | | ||
|rowspan="1" colspan="2" | | <div class="CellBody"> </div> | ||
| rowspan="1" colspan="2" | | |||
<div class="CellBody"><span style="font-style: normal; text-decoration: none; text-transform: none; vertical-align: baseline">'''<font color="#000000">Paste Function</font>'''</span>-Pastes a previously copied function into the window. The pasted function has a different color than the first function displayed in the window.</div> | |||
|- | |- | ||
| | | | ||
|rowspan="1" colspan="2" | | <div class="CellBody"><span style="font-style: normal; text-decoration: none; text-transform: none; vertical-align: baseline">'''<font color="#000000">Views</font>'''</span></div> | ||
| rowspan="1" colspan="2" | | |||
<div class="CellBody"><span style="font-style: normal; text-decoration: none; text-transform: none; vertical-align: baseline">'''<font color="#000000">Modify Graph Features</font>'''</span>-Allows you to customize the appearance of the graph.</div> | |||
|- | |- | ||
| | | | ||
|rowspan="1" colspan="2" | | <div class="CellBody"> </div> | ||
| rowspan="1" colspan="2" | | |||
<div class="CellBody"><span style="font-style: normal; text-decoration: none; text-transform: none; vertical-align: baseline">'''<font color="#000000">Reset Range to Default</font>'''</span>-TBD.</div> | |||
|- | |- | ||
| | | | ||
|rowspan="1" colspan="2" | | <div class="CellBody"> </div> | ||
| rowspan="1" colspan="2" | | |||
<div class="CellBody"><span style="font-style: normal; text-decoration: none; text-transform: none; vertical-align: baseline">'''<font color="#000000">Reset Graph to Original</font>'''</span>-TBD.</div> | |||
|- | |- | ||
|'''Help''' | | | ||
|rowspan="1" colspan="2" |Displays online help | <div class="CellBody"><span style="font-style: normal; text-decoration: none; text-transform: none; vertical-align: baseline">'''<font color="#000000">Help</font>'''</span></div> | ||
| rowspan="1" colspan="2" | | |||
<div class="CellBody"><span style="font-style: normal; text-decoration: none; text-transform: none; vertical-align: baseline">'''<font color="#000000">Help Topics</font>'''</span>-Displays online help topics.</div> | |||
|} | |} | ||
'''To generate 3D intensity graphs of all slices in a dataset at a specific point'''<br /> | |||
1 Open an image.<br /> | |||
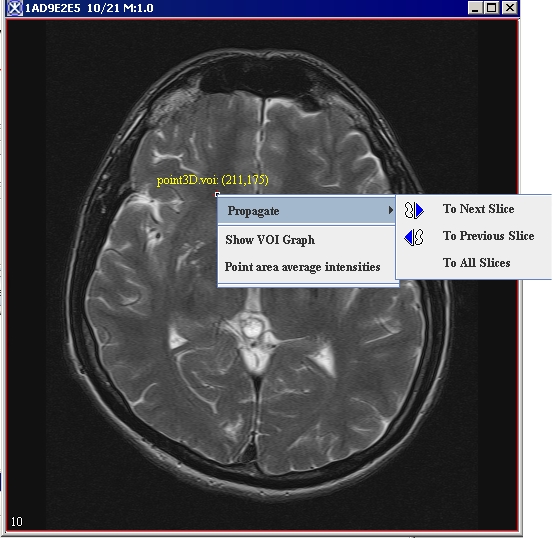
2 Draw a point VOI on the image (Figure 12).<br /> | |||
3 Select the VOI.<br /> | |||
4 Do one of the following:<br /> | |||
*Select the Propagate VOI to all slices icon.<br /> | |||
*Select VOI > Propagate > To All Slices. <br /> | |||
*Right-click on the VOI, then select Propagate > To All Slices (Figure 12).<br /> | |||
5 Right-click on the VOI and select Show VOI Graph (Figure 12).<br /> | |||
{| border="1" cellpadding="5" | |||
|+ '''Figure 12. Point VOI''' | |||
|- | |||
| | |||
<div style="font-style: normal; font-weight: normal; margin-bottom: 0pt; margin-left: 0pt; margin-right: 0pt; margin-top: 0pt; text-align: left; text-decoration: none; text-indent: 0pt; text-transform: none; vertical-align: baseline"><font color="#000000"> <br /></font></div> | |||
= | <br clear="all" /> | ||
{| | |||
| | |||
[[Image:PointVOIPropagate.jpg]] | |||
|} | |||
To | '''To generate 3D intensity graphs of specific areas'''<br /> | ||
1 Open an image.<br /> | |||
2 Delineate a VOI on the image using the 3D rectangular VOI icon.<br /> | |||
3 Select the VOI. Then, do one of the following:<br /> | |||
*a Select VOI > Graph and either of the following in the MIPAV window:<br /> | |||
** ''2.5D Total Intensity'' -To generate a graph of the sum of the intensity values of the area delineated by the VOI per slice.<br /> | |||
** ''2.5D Average Intensity'' -To generate a graph of the average of the intensity values of the VOI region.<br /> | |||
*b Right-click the VOI, and then select Graph and one of the following commands in the MIPAV window:<br /> | |||
** ''2.5D Total Intensity'' -To generate a graph of the sum of the intensity values of the area delineated by the VOI per slice.<br /> | |||
** ''2.5D Average Intensity'' -To generate a graph of the average of the intensity values of the VOI region.<br /> | |||
** ''2.5D Total Intensity with Threshold'' -TBD.<br /> | |||
** ''2.5D Average Intensity with Threshold'' -TBD.<br /> | |||
The Intensity Graph window (Figure 11) opens.<br /> | |||
[[ | [[Customizing the appearance of graphs - Modify graph dialog box]] | ||
Revision as of 20:22, 21 February 2012
MIPAV allows you to generate intensity profiles, or contour VOI graphs, for VOI contours. For delineated VOIs, you can generate 2D, 3D, or 4D intensity graphs. You can also generate a 3D intensity graph at a specific point across all slices in a dataset. For information on how to contour a VOI, refer to Chapter 1, "Segmenting Images Using Contours and Masks,"
Generating contour VOI graphs
Contour VOI graphs display the intensity values of the selected contour's boundary in the Contour VOI Graph window (Figure 10). You can generate either 2D or 3D contour VOI graphs.
To generate 2D contour VOI graphs
1 Open an image.
2 Delineate a 2D VOI on the image using one of the 2D icons in the MIPAV window.
|
File
|
Open Graph-Opens a PLT file that contains graph data. When you select this command or press Ctrl O on the keyboard, the Open Graph Data dialog box appears.
| |
|
Save Graph-Saves the graph data in a PLT file. When you select this command or when you press Ctrl S on the keyboard, the Save dialog box opens.
| ||
|
Print Graph-Allows you to print the graph. When you select this command or press
Ctrl P, the Print dialog box opens. | ||
|
Close Graph-Closes the Intensity Graph window. To close the window, you can also press Ctrl X on the keyboard.
| ||
|
Edit
|
Delete Function-Allows you to delete a specific function. However, you cannot delete a function if it is the only function displayed in the window.
| |
|
Copy Function-Copies a function that is currently displayed in the window.
| ||
|
Paste Function-Pastes a previously copied function into the window. The pasted function has a different color than the first function displayed in the window.
| ||
|
Views
|
Modify Graph Features-Allows you to customize the appearance of the graph.
| |
|
Reset Range to Default-[TBD]
| ||
|
Reset Graph to Original-[TBD].
| ||
|
Help
|
Help Topics-Displays online help topics.
| |
3 Select the VOI.
As an option, copy the VOI to other slices in the dataset by selecting VOI > Propagate and one of the following commands:
- To Next Slice
- To Previous Slice
- To All Slices
4 Do one of the following:
- Select VOI > Graph > Boundary Intensity in the MIPAV window.
- Right click on the VOI and then select Graph > Boundary Intensity.
- The Contour VOI Graph window (Figure 10) opens.
To generate 3D contour VOI graphs
1 Open an image.
2 Delineate a VOI on the image using the 3D rectangular VOI icon, in the MIPAV window.
3 Select the VOI.
As an option, copy the VOI to other slices in the dataset by selecting VOI > Propagate and one of the following commands:
- To Next Slice
- To Previous Slice
- To All Slices
4 Do one of the following:
- Select VOI > Graph > Boundary Intensity in the MIPAV window.
- Right-click on the VOI and then select Graph > Boundary Intensity.
The Contour VOI Graph window (Figure 10) opens. This window displays a graph of the intensity values of the selected contour's boundary.
Generating intensity graphs
Intensity profiles, or graphs, present information on the intensity values of the VOI region in an image. The intensity graph appears in the Intensity Graph window (Figure 11).
To generate 2D intensity graphs
1 Open an image.
2 Delineate a 2D VOI on the image using one of the 2D icons in the MIPAV window.
<
3 Select the VOI.
As an option, copy the VOI to other slices in the dataset by selecting VOI > Propagate and one of the following commands:
- To Next Slice
- To Previous Slice
- To All Slices
4 Do one of the following:
Select VOI > Graph in the MIPAV window and either of the following:
- 2.5D Total Intensity -To generate a graph of the sum of the intensity values of the VOI region.
- 2.5D Average Intensity -To generate a graph of the average of the intensity values of the VOI region.
Right-click on the VOI and then select Graph and one of the following commands:
- 2.5D Total Intensity -To generate a graph of the sum of the intensity values of the area delineated by the VOI per slice.
- 2.5D Average Intensity -To generate a graph of the average of the intensity values of the VOI region.
- 2.5D Total Intensity with Threshold -TBD.
- 2.5D Average Intensity with Threshold -TBD.
The Intensity Graph window (Figure 11) opens.
|
File
|
Open Graph-Opens a PLT file that contains graph data. When you select this command or press Ctrl O on the keyboard, the Open Graph Data dialog box appears.
|
|
|
|
Save Graph-Saves the graph data in a PLT file. When you select this command or when you press Ctrl S on the keyboard, the Save dialog box opens.
| |
|
|
Print Graph-Allows you to print the graph. When you select this command or press
Ctrl P, the Print dialog box opens. | |
|
|
Close Graph-Closes the Intensity Graph window. To close the window, you can also press Ctrl X on the keyboard.
| |
|
Edit
|
Delete Function-Allows you to delete the function that you select. However, you cannot delete a function if it is the only function displayed in the window.
| |
|
|
Paste Function-Pastes a previously copied function into the window. The pasted function has a different color than the first function displayed in the window.
| |
|
Views
|
Modify Graph Features-Allows you to customize the appearance of the graph.
| |
|
|
Reset Range to Default-TBD.
| |
|
|
Reset Graph to Original-TBD.
| |
|
Help
|
Help Topics-Displays online help topics.
| |
To generate 3D intensity graphs of all slices in a dataset at a specific point
1 Open an image.
2 Draw a point VOI on the image (Figure 12).
3 Select the VOI.
4 Do one of the following:
- Select the Propagate VOI to all slices icon.
- Select VOI > Propagate > To All Slices.
- Right-click on the VOI, then select Propagate > To All Slices (Figure 12).
5 Right-click on the VOI and select Show VOI Graph (Figure 12).
|
To generate 3D intensity graphs of specific areas
The Intensity Graph window (Figure 11) opens.
|