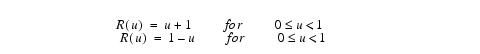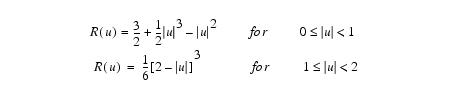Image resampling is an interpolation process in which anisotropic voxels (in the Z direction) are resampled into isotropic-sized voxels. The new voxels are formed by taking the weighted combination of the source voxels within a defined neighborhood of the reference voxel. Three interpolation methods are supported: linear, cubic convolution, and cubic B-spline.
Refer to "Optimized Automatic Registration 3D" for resampling an image at various orientations using a choice of interpolation methods.
Background
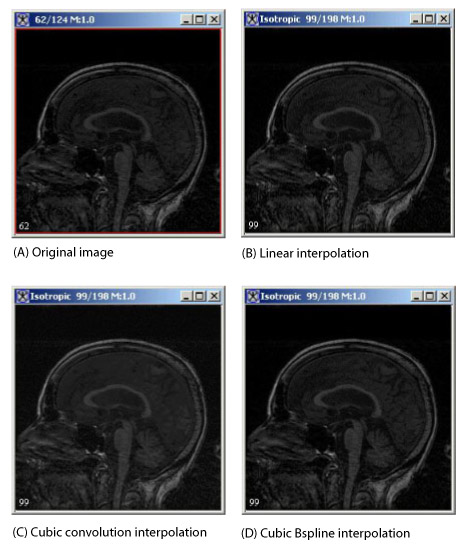
This section shows the equations that MIPAV uses for the three interpolation methods for the algorithm. Figure 1 shows an original image and the resulting images after linear, cubic convolution, and cubic B-spline interpolation are applied, see also "Interpolation methods used in MIPAV".
Linear interpolation
The equations for linear interpolation are the following:
Cubic convolution interpolation
The equations that apply to cubic convolution interpolation are:
Cubic B-spline interpolation
MIPAV uses the following equations for cubic B-spline interpolation:
References
None.
Image types
You can apply this algorithm to all image data types except RGB and complex. This algorithm can not be applied to 2D and 4D images.
Applying the Reslice-Isotropic Voxels algorithm
To run this algorithm, complete the following steps:
- Open an image.
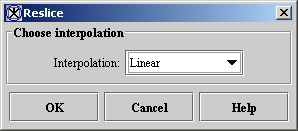
- Select Algorithms > Reslice-Isotropic Voxels. The Reslice dialog box (Figure 2) opens.
- Select an interpolation method in Interpolation.
- Click OK.
- A status message appears. When the algorithm is complete, the results appear in a new image window.
|
Interpolation
|
Specifies the type of interpolation to use when applying this algorithm. You can select one of the following: linear, cubic, or cubic B-spline.
|
|
|
OK
|
Applies the Reslice-Isotropic Voxels algorithm according to the specifications in this dialog box.
| |
|
Cancel
|
Disregards any changes you made in this dialog box; closes the dialog box.
| |
|
Help
|
Displays online help for this dialog box.
| |