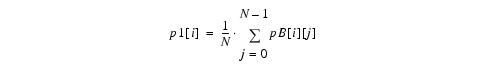The Registration: Landmark-Least Squares algorithm provides a way for registering an image to the reference image by using corresponding points placed in both images. This algorithm works on images requiring rotation and translation, but it does not work on images requiring scaling, because this is a rigid transformation based on two homologous landmark datasets.
Background
The algorithm relates the two corresponding point sets on the image to be registered and on the reference image using the following equation:
where
- pA[i][j] = the point set of the reference image
- pB[i][j] = the point set of the image to be registered
- i = a value from 0 to the number of dimensions - 1
- j = a value from 0 to the number of user-placed corresponding points - 1
- R = a rotation matrix
- T = a translation vector
- No[i][j] = a noise vector
This algorithm calculates a least-squares solution of R and T, which is based on a singular value decomposition of a 2 x 2 matrix in 2D or a 3 x 3 matrix in 3D. It, first, calculates the centroid p1[i] in the image to be registered:
It, then, calculates the centroid p2[i] in the reference image:
where N = the number of corresponding user points.
The algorithm, next, calculates the difference between the points and the centroid voxel in the image to be registered (q1[i][j]):
and then the difference between the points and centroid voxel in the reference image (q2[i][j]):
The algorithm then performs the following steps:
- Calculates the 2 x 2 or 3 x 3 matrix:
- Performs the singular value decomposition of H. That is:
- Calculates the following:
- Calculates the determinant of X (refer to the following table).
- If the determinant is 1, the algorithm succeeded and the rotation matrix
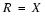 .
. - If the determinant is -1 and the images are 3D, then the singular values of matrix H must be examined. If one and only one of the three singular values is 0 and the two singular values are unequal, then the case is coplanar, but not colinear. It is made to work by simply changing the sign of the third column of the V matrix to form Vp and obtain
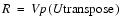 .
.
- Calculates the translation vector:
- Sets the first dim elements of the last column of the transformation matrix to T.
- Copies R into the upper left dim by dim elements of the transformation matrix.
- Sets the last row of the transformation matrix to 0,0,1 in the 2D case or to 0,0,0,1 in the 3D case.
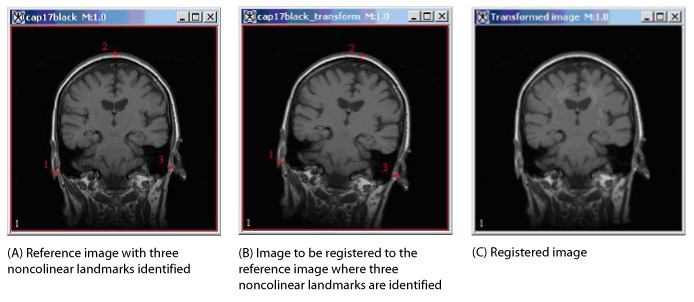
- A bilinear or trilinear transformation is used with the given transformation matrix to transform the target image into the resulting image (Figure 1). Refer to "Interpolation methods used in MIPAV".
|
Image type
|
If this is true . . .
|
Then . . .
|
Comments
| ||
|
Determinant
|
Matrix H
|
Success
|
Failure
| ||
|
2D images
|
1
|
X
|
Rotation matrix
R = X | ||
|
-1
|
Has no zero singular values
|
X
|
Data too noisy
| ||
|
-1
|
Has one singular value
|
X
|
Data is colinear
| ||
|
3D images
|
1
|
X
|
|||
|
-1
|
Has no zero singular values
|
X
|
Data too noisy
| ||
|
-1
|
Has one zero singular value and the other two singular values are unequal
|
X
|
|||
|
-1
|
Has two equal singular values
|
X
|
Colinear
| ||
Image types
You can apply this algorithm to 2D and 3D grayscale and color images.
Special notes
The following notes apply:
- Do not use this algorithm in cases where an image must be scaled.
- For 2D images, you must identify at least three noncollinear points.
- For 3D images, you must identify at least four noncollinear points.
Reference
Refer to the following reference for more information:
"Least-Squares Fitting of Two 3-D Point Sets" by K.S. Arun, T.S. Huang, and S.D. Blostein, IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence, Vol. PAMI-9, No. 5, September, 1987,
pp. 698-700.
Applying the Landmark-Least Squares Registration algorithm
To run this algorithm, complete the following steps:
- Open two images: the target image and the reference image. When you apply this algorithm, MIPAV registers the target image to the selected reference image.
- Perform, as an option, any other image processing, except scaling, on both images.
- Place a minimum of three points in 2D images or four points in 3D images in the reference image. The points must not be colinear.
Note: Three-dimensional (3D) images can handle cases that are coplanar but not colinear.
- Place the corresponding points in the target image. Note that the dialog box shows the last image clicked on as the target image.
Tip: Make sure that you delineate the points on the target image in the same order as on the reference image. That is, point 1 on the reference image should correspond to point 1 on the target image, point 2 on the reference image should correspond to point 2 on the target image, etc.
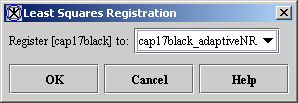
- Select Algorithms > Registration > Landmark - Least Squares. The Least Squares Registration dialog box (see Figure 2) appears.
- Select the name of the target image in the Register to box if it is not already present.
- Click OK.
- The algorithm begins to run. A pop-up window appears with the status.
- When the algorithm finishes running, the pop-up window closes, and the registered image appears in the Transformed Image window.
|
Register [name of source image] to [name of reference image]
|
Displays a set of possible reference images. This box registers the image to be registered to the selected reference image.
|
|
|
OK
|
Applies the algorithm according to the specifications in this dialog box.
| |
|
Cancel
|
Disregards any changes that you made and closes the dialog box.
| |
|
Help
|
Displays online help for this dialog box.
| |