This algorithm defines the edges of an image by calculating the nonmaximum suppression of an image at a user-defined scale. An edge is defined as the union of points for which the gradient magnitude assumes a maximum in the gradient direction.
Image types
The nonmaximum suppression image can be generated from 2D, 2.5D, and 3D black-and-white images. However, the option to output an edge image is only available for black-and-white 2D images.
Applying the Nonmaximum Suppression algorithm
To run this algorithm, complete the following steps:
- Open an image.
- Perform, as an option, any other image processing, such as improving the contrast, on the image.
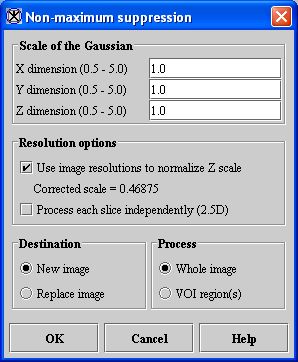
- Select Algorithms > Filter (spatial) > Nonmaximum suppression. The Nonmaximum suppression dialog box (Figure 1) opens.
- Complete the information in the dialog box.
- Click OK. The algorithm begins to run.
- A pop-up window appears with the status. The following message appears
- "Calculating the Nonmaximum suppression."
- When the algorithm finishes running, the pop-up window closes. Depending on whether you selected New image or Replace image, the results appear in a new window or replace the image to which the algorithm was applied.
| Note: For 2D images, if you selected Output edge image, a new window with an edge image appears. |
Nonmaximum Suppression dialog box
|
X dimension
|
Indicates the scale of the Gaussian in the X direction (the default value is 1.0).
|
|
|
Y dimension
|
Indicates the scale of the Gaussian in the Y direction (the default value is 1.0).
| |
|
Z dimension
|
Indicates the scale of the Gaussian in the Z direction (for 3D images only). The default value is 1.0.
| |
|
Use image resolutions to normalize 'Z' scale
|
Normalizes the Z scale to compensate for the difference if the voxel resolution in distance per pixel is greater between slices than the voxel resolution in-plane (for 3D images only, the default value is enabled).
| |
|
Process each slice independently
|
Calculates nonmaximum suppression for each slice of the dataset independently (for 3D images only the default value is enabled).
| |
|
New image
|
Shows the results of the algorithm in a new image window (default choice). If selected, an output edge image appears in a second new window.
| |
|
Replace image
|
Replaces the current active image with the results of the algorithm.
| |
|
Whole image
|
Applies the algorithm to the whole image (default choice).
| |
|
VOI region(s)
|
Applies the algorithm inside VOIs. Outside VOIs, the pixel values are unchanged.
| |
|
OK
|
Applies the algorithm according to the specifications in this dialog box.
| |
|
Cancel
|
Disregards any changes that you made iin the dialog box and closes this dialog box.
| |
|
Help
|
Displays online help for this dialog box.
| |